Push notifications are brief, actionable updates that appear on a user’s device (often without them being actively engaged in the app or website). In essence, they provide real-time nudging designed to pull the user back into your product, help them execute meaningful actions, or simply remind them that your app exists.
In a digital ecosystem where mobile-first experiences are the priority, these real-time nudges become one of the most immediate ways for brands to effectively engage users. Timely notifications are important for creating app sessions and retention, but they create a nudge to conversions, remind users of incomplete journeys, and generate personalized, moment-driven experiences that actually stick.
Whether you are promoting a new campaign, announcing a feature update, or targeting lapsed users, these updates give you real estate on your audience’s home screen. That’s kind of a big deal.
What are Push Notifications?
They are instant messages sent by apps or websites to a user’s device, even if the app is not in use. Depending on the device, these notifications will pop up on the lock screen, notification tray, or browser window.
They are built to catch attention, share an important update, elicit action, or simply keep your brand in users’ minds.
There are three primary types of push notifications:
- Mobile Push Notification
- Web Push Notification
- In-App Notification
Each one has a unique role in the user journey in their own right and all of which help contribute to higher conversions and a long-lasting relationship.
The Importance of Push Notifications
Push notification provide more than just a friendly reminder; these notifications can be a strategic lever for growth. Industry sources suggest:
- Open rates for mobile push notifications are sometimes reported as high as 90%
- Apps sending push notification have 3x higher retention rates
- Well-timed push campaigns can result in as much as 88% higher app engagement
Push notification deliver contextual communication at almost the exact moment it is needed. Whether it’s completing checkout for a shopper, letting users know new content is available, or celebrating an event milestone, push notification gives you one direct line to your users, without them actually having to open the app.
Types of Push Notifications
Now, let’s identify and discuss the varieties of push notifications and how we utilize them in the mobile space today.
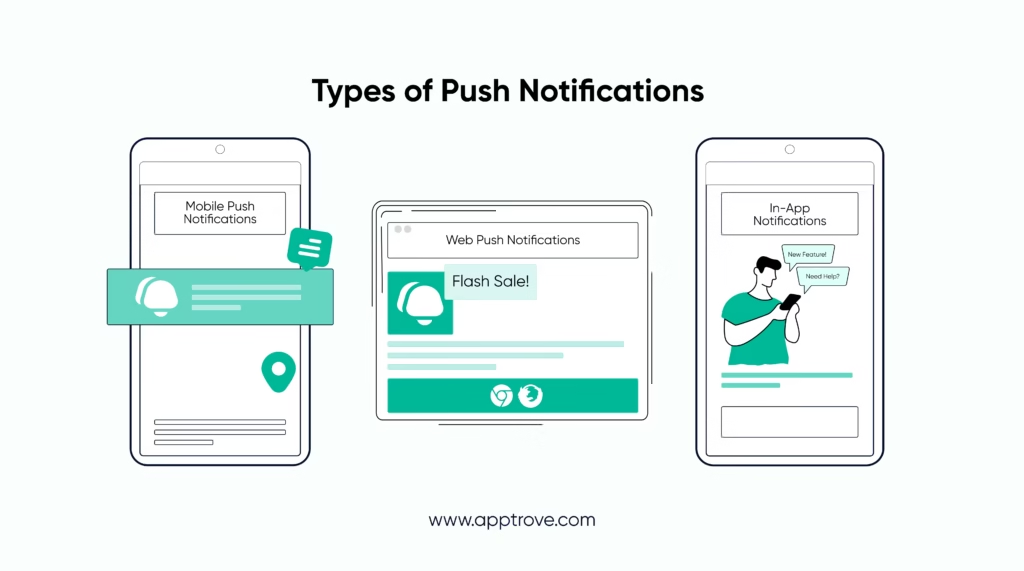
Mobile Push Notifications
Mobile trigger-based messages are messages sent to a user’s mobile device (i.e., smartphone or tablet) through a mobile app. These notifications will either appear on the device’s lock screen or the notification center (this depends on the user’s operating system and settings).
Mobile push notifications have a broad range of versatility that makes them a fantastic tool. You can:
- Notify users about offers, updates, or events
- Encourage users to re-engage and drive users back into the app
- Customize notifications based on past behaviors, location, and preferences
Mobile push notifications are opt-in, in that users must explicitly permit receiving them, rendering mobile push notifications a high-intent channel. If a user opts to receive notifications, not only does that user want to receive them, but they have also communicated intent and interest in your content or services.
Web Push Notifications
Web Notifications are conceptually similar, but are browser-specific. They are clickable messages sent via a desktop or mobile web browser, even when the user is not visiting your website. They are well suited for:
- Bringing users back to your website
- Announcing flash sales, restocks, or new blog content
- Real-time service updates or reminders
For brands that don’t have an app or want to engage with users outside of an app experience, web push notification offer a great weapon that too often goes underused.
In-App Notifications
In-app notifications are notifications shown while in use, when the user is actively using your app. These notifications are contextual messages with a real-time component based on actions or behaviors from users inside the app.
In-app notifications are useful for:
- Onboarding new users with tooltips/welcome flows
- Announcing new features
- Prompting upgrades, subscriptions, or referrals
- Helping new users move through a multi-step process
In-app notifications are the most effective and reliable way to communicate at the moment, whether you’re onboarding a new user or announcing a new feature, because in-app notifications don’t require user opt-in like push does. In-app notifications allow you to communicate exactly when and where users are most engaged.
Key Advantages of Push Notifications
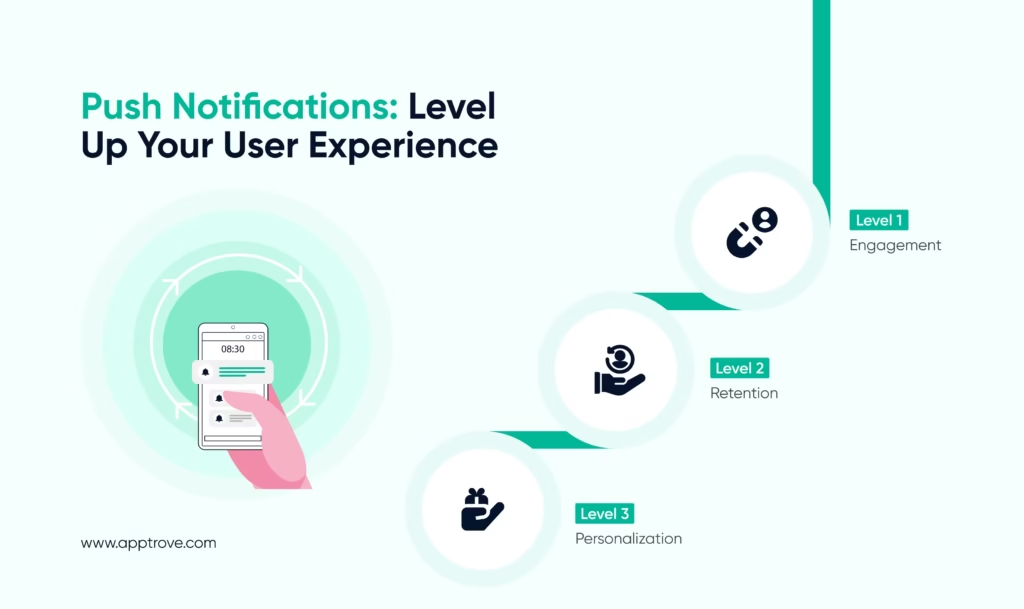
User Engagement
When thoughtfully timed and personalized, trigger-based messages significantly improve user engagement. They serve as a reminder of the value of your app and can prompt users to come back into the experience. They give users timely notifications about opportunities that they likely wouldn’t want to miss.
They cut through the clutter of the digital environment, helping keep a healthy and engaging relationship between the user and the app.
Retention
Users who are quiet can disappear quickly, and if you re-engage them early enough, you can help retain those users. One of the best channels for retaining users and decreasing churn levels is trigger-based messages. Re-engagement messages, loyalty reminders, incentives based on past behavior, or something completely personalized can easily prime the user to come back and use an app after they delete it from their device or even forget about it!
A smart push strategy is like having a conversation, keeping it two-way, timely and relevant, is built on trust, which can lead to long-term retention.
Enhanced Personalization
If you have the right data signals (location, usage history, preferences, etc.), then push notification slice personalization in hyper-personalized formats. This leads to better open rates, higher conversion, and helps establish a deeper connection between the brand and the user.
Now imagine reminding a user about items in an abandoned cart, or offering a discount for a user on their birthday, or letting a user know something they have opted in to follow has an updated event. Personalization makes push a pleasure, not a prohibition.
Best Practices for Effective Push Notifications
Fundamental Considerations for Sending Outstanding Push Notifications.
Creating a great push campaign is not purely about frequency or clever copy. It is about having some strategy behind it. Here are some fundamentals:
Get Opt-In Properly
Be respectful of privacy. The user should always be asked for push permission at the appropriate time, after experiencing the value of the app and not at install time.
Keep It Brief and to the Point
You only have so much time to capture someone’s attention. Target 10-15 words and have a clear call-to-action. Use emojis if you would like, but do not get carried away.
Segment Your Audience
Not every message you send will be relevant to each user. Segment your audience by behavior, location, device type or app version to help with relevancy. Define specific user segments to create personalized push journeys that feel timely and valuable.
Timing Matters
Timing is a factor. An alert goes out at peak times, will perform better than one sent at midnight. Always be mindful of user patterns & time zone preferences.
Test & Learn
Use A/B testing to compare variations & measure performance. You should ask while experimenting with copy, time, visuals, or even frequency, to find what is best received.
How Push Notifications Work With Attribution
A crucial inquiry that app marketers have: How do I evaluate the true value of my push notification campaigns?
With clever, privacy-driven tracking, modern attribution platforms allow you to see which push campaigns lead to installs, sessions, or revenue and which ones are not performing.
Whether you use mobile push notifications, web push notifications, or in-app notifications, connecting these models to attribution will allow you to:
- Evaluate the performance of the campaign level
- Measure post-click and post-view conversions
- Build a better push strategy based on outcomes and the data available
Push is about more than sending messages; it is about knowing the results of any kind of interaction.
The Future of Push Notifications
The evolution of the push ecosystem is happening rapidly. Rich media (images, videos, carousels), interactive content (buttons, replies), and AI-driven personalization are constantly expanding the possibilities to engage users with push notifications.
Meanwhile, evolving privacy regulations and changing user expectations impose stricter limitations and necessitate smarter, permission-based communication.
The future of push notifications is:
- Smarter: powered by contextual, AI-driven insights
- More respectful: compliant and opt-in based
- Cross-platform: mobile apps, browsers, wearables
- Action-oriented: supporting meaningful, timely user actions
Modern platforms are evolving to support this future, combining advanced measurement, segmentation, and campaign tracking for scalable push performance.
Final Remarks
Push notifications are much more than a feature; they are a major growth driver.
If done well, push notifications increase user engagement, retention, revenue and long-term relationships with users. If done poorly, push notifications can annoy a user causing them to uninstall.
To turn your push campaigns into a foundational driver of success for your app, pair behavioral insights with timing, personalization and targeting to maximize impact.
Apptrove gives you all the tools to optimize mobile push notifications, experiment with web push notifications, and perfect your in-app notifications…while being privacy-first and future-proof!