The rapid growth of digital advertising has resulted in billions of impressions being served each day across websites, apps, and connected devices. The ad server is the core of this new growth. The ad server stores the ads, identifies which ads to serve, and measures the ad performance. As the digital environment continues to evolve to include many different ad formats, real-time bidding (RTB), and advanced targeting technology, the role of the ad server has also evolved from a basic delivery mechanism to a more complex and sophisticated platform used to gather campaign intelligence and to optimize campaigns.
A single page load now stimulates many hundreds of processes that trigger decisions about the ad to be served within a time frame of 100 to 150 milliseconds. Therefore, it is very important for publishers, advertisers, and agencies alike, to understand how decision-making about ad placement works in this increasingly technical environment.
What is an Ad Server?
An ad server is a centralized system that stores all of the creative assets (ads), evaluates all of the targeting criteria (who sees the ad, when, where), and serves the most relevant ads to the right person at the right time. In addition to delivering ads, the ad server also tracks the number of impressions served, the number of clicks to the ad, and the engagement data associated with each ad (clicks, time spent on the site, purchase history).
Ads are primarily purchased and sold through automated buying platforms, and as such, the ad server is the foundation of scalability for digital marketing operations. With its intelligence, the ad server enables advertisers
How an Ad Server Works Behind the Scenes
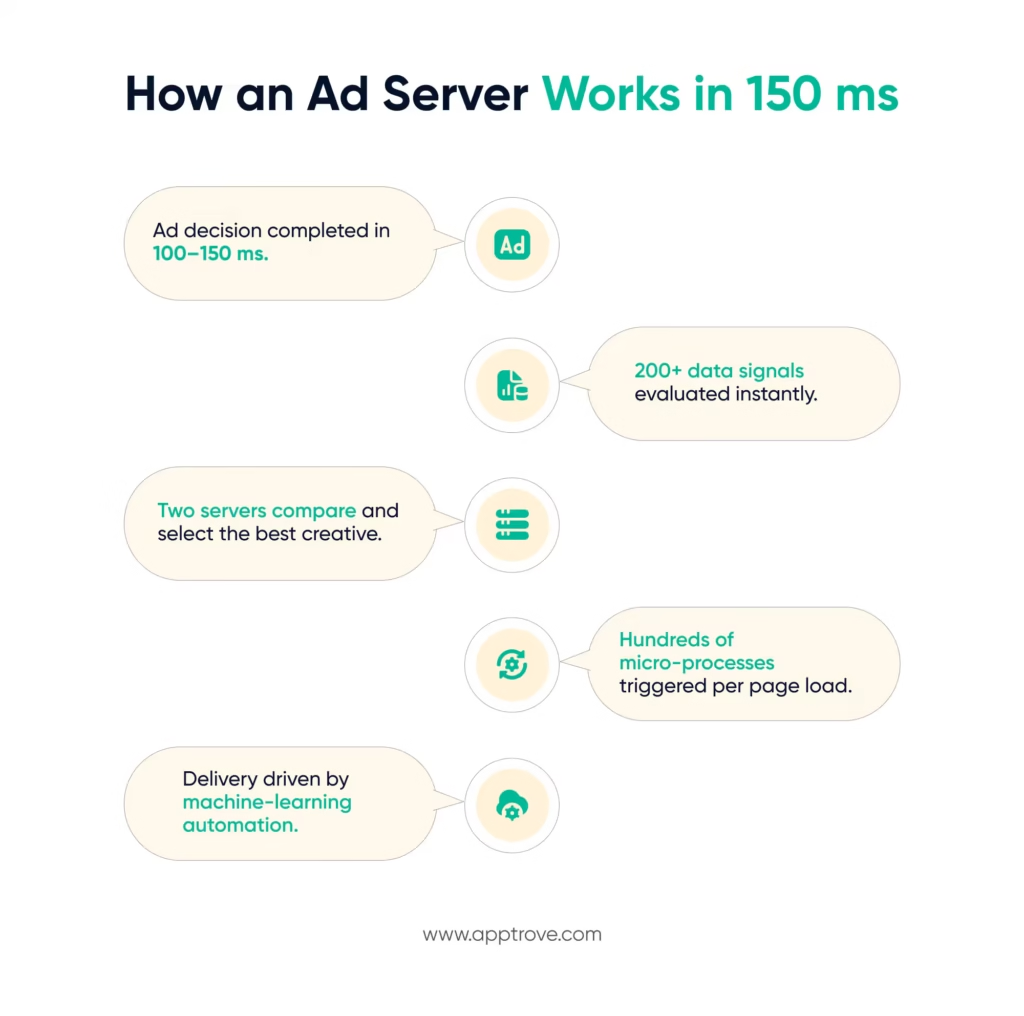
When you open an application or a website, there will be a request sent for a free ad slot that is created at the same time. The ad server will consider the contextual information associated with your request:
- The type of device and operating system you’re using
- Your geographic location
- The page URL you’re viewing or the screen of the application (depending on what you are using to view).
- The language you have set up on your device
- Any identifiable information about you as the user (if and where applicable)
- Any behaviors that may pertain to interest segmentation categories.
By collecting these signals, it can determine what creative to send (what) ‘creative’ to ‘send’ to the user based on campaign budget, targeting criteria, and delivery schedule. The second server on the advertising side will look at all available creatives and will select the most appropriate one prior to sending it to the publisher for placement.
Since all of this occurs instantaneously, there is no possibility of relying on any manual processes for ad delivery; it all occurs automatically via preconfigured procedures and optimization through the use of algorithms and machine-learning technologies.
Programmatic Ad Serving and Real-Time Bidding
When you open an application or a website, there will be a request sent for a free ad slot that is created at the same time.
The ad server will consider the contextual information associated with your request:
- The type of device and operating system you’re using
- Your geographic location
- \The page URL you’re viewing or the screen of the application (depending on what you are using to view).
- The language you have set up on your device
- Any identifiable information about you as the user (if and where applicable)
- Any behaviors that may pertain to interest segmentation categories.
By collecting these signals, it can determine what creative to send (what) ‘creative’ to ‘send’ to the user based on campaign budget, targeting criteria, and delivery schedule. The second server on the advertising side will look at all available creatives and will select the most appropriate one prior to sending it to the publisher for placement.
Since all of this occurs instantaneously, there is no possibility of relying on any manual processes for ad delivery; it all occurs automatically via preconfigured procedures and optimization through the use of algorithms and machine-learning technologies.
First-Party vs. Third-Party Ad Servers
Although modern platforms can handle both roles, distinctions remain important.
First-Party (Publisher-Side)
First party ad servers manage ad inventories for the publisher; assign priority to campaigns across ad types; and identify which advertiser has access to fill each slot. They focus on optimizing publisher revenue; forecasting impressions available for purchase; enforcement of frequency and placement rules for ads; generating ad tags; and managing direct deal advertisements between the publisher and an advertiser. Publishers use first-party ad servers to help ensure that their most valued opportunities are being fulfilled with the most relevant campaign(s).
Third-party ad servers are an advertiser’s central point for managing creative assets and reporting of creative run on all channels.
Advertisers use third-party ad servers to host multiple creative variations; apply frequency caps; optimize the pacing of delivery; track conversions for all placements; and maintain unified reporting instead of relying on individual publisher’s (publisher) performance. This allows for increased transparency and cross-channel insights (cross-channel attribution).
Hosted vs. Self-Hosted Ad Servers
Select an appropriate environment based on control, expense, and expertise (controlled, low-cost, and high-technical-expertise).
Hosted Solutions
With a hosted solution, you’re using a platform hosted by another company. The platform will typically be very reliable and easy to use. Hosted solutions are also an excellent choice for organizations that do not have engineering capabilities to develop and maintain their own solutions but require technical support and ease of use.
Open-Source / Self-Hosted Solutions
Organizations that elect to use self-hosted platforms (or build their own) will have the most control (full) over their data and how or if they modify their systems. The drawback to a self-hosted or open-source solution is that one would need to have their own internal technical expertise to support and maintain the solution. In addition, self-hosted solutions traditionally will be more cost-efficient long-term and allow for complete customization of features.
Metrics for Measuring Ad Servers
As ad servers are integral to spend, attribution, and performance, they must report accurate numbers. Metrics generally associated with ad servers include the following:
- Ad Impressions and Viewable Ad Impressions
- CPM, eCPM, vCPM
- Fill Rates & Number of Requests
- Click Rates and CTR
- CPC and CPA
Differences Between 2 Reporting Systems
Because there are billions of daily events recorded for each ad served, the amount of potential revenue or budget impact associated with even minute flaws in measurement can be significant, so it is vital to implement consistent measurement across all ad servers.
Ad Server vs. Ad Network vs. Ad Exchange
Clarifying these distinctions serves to eliminate the confusion present within the programmatic ecosystem.
Ad Network
The ad network aggregates a publisher’s advertising assets (inventory) and then sells that inventory to advertisers; it is responsible for managing the supply of publisher inventory, segmenting it into different categories by audience(s), and negotiating the price for the inventory.
Ad Exchange
The ad exchange is an automated auction marketplace where buyers and sellers of individual impressions conduct real-time transactions with one another.
Ad Server
The ad server manages the creation of creative assets (ads), determines which ad will be served to an audience, enforces the rules of an advertising campaign, and collects data about the performance of ads.
Evaluating the Ad Serving Solution
When evaluating an ad serving solution, businesses should consider:
- What level of customization is required by the business?
- Is it desirable to have both first and third-party capabilities available?
- What APIs or other forms of technical extensibility are required?
- How in-depth will the reporting of data be and who owns the data?
- Will the ad serving solution support advanced formats (video, native, CTV)?
Finding the right ad serving solution will lay the groundwork for the streamlining of business operations, accurate measurement of ad performance, and intelligent allocation of advertising budgets.
Key Semrush-Style Questions People Also Ask
Examples of common questions about digital advertising include:
- How do ad servers work in the digital advertising industry?
- How does an ad server determine which ad to display?
- What is the difference between first-party and third-party ad servers?
- Is an ad server a demand-side platform?
- What is the time frame for an ad server to deliver ads to users?
These questions indicate continued interest in automation, privacy, and optimisation within the ad technology space.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of an ad server?
An advertisement server’s key benefit is the ability to save creative advertisements, select the optimal advertisement instantly and analyze the effectiveness of advertisement performance through multiple locations.
2. How fast does ad serving happen?
Advertisement server responses occur relatively quickly; most responses will be received from an advertisement server within 100-150 milliseconds and before the page has completed loading.
3. Why are first-party and third-party servers different?
First-party and third-party advertisement servers differ because first-parties are utilized by publishers to control their inventories, while third-party servers provide advertisers with complete reporting and control over their creative advertisements.
4. Does every programmatic ad use real-time bidding?
All programmatic advertisements may not use real-time bidding (RTB) for placement. However, most programmatic ads will go through RTB channels, while other options include direct deals and private marketplace (PMP) buys.
5. Is a self-hosted ad server better?
Self-hosted advertisement servers provide full control and ownership of your data; however, they require you to have robust in-house technical support capabilities.