E-commerce and m-commerce are crucial platforms transforming how businesses interact with consumers and handle transactions.
E-commerce involves buying and selling through desktop or laptop websites, while m-commerce focuses on mobile-based transactions via mobile phones and tablets.
As mobile commerce continues to surge, it’s projected to cross $4.5 trillion by this year. This growth will account for about 70% of e-commerce sales.
Given this explosive shift, understanding the distinct roles of both platforms is pivotal. Each offers unique advantages, but their user experience, technology, and consumer behavior make them suitable for different situations.
For business leaders, knowing when and how to leverage both e-commerce and m-commerce is key to effectively reaching and converting customers.
In this blog, we’ll explore the key differences between e-commerce and m-commerce and how you can leverage m-commerce to stay competitive.
What Is E-Commerce?
E-commerce stands for electronic commerce and refers to buying and selling products or services online.
For instance, the leading e-commerce retailer Amazon uses its desktop platform to offer customers an array of products, integrating personalized recommendations, payment gateways, and quick delivery options.
Benefits of E-Commerce
The key benefits of e-commerce include –
- Global Reach: Businesses can connect with a broader audience, expanding their client base beyond physical locations.
- Cost-Effective Operations: E-commerce minimizes the need for physical stores, decreasing overhead and operational costs.
- 24/7 Availability: Customers can place orders anytime, regardless of business hours. This ease of buying can boost conversion rates.
- Data-Driven Insights: Businesses can track and analyze customer behavior to optimize product offerings and marketing strategies.
- Personalization: Advanced algorithms can help tailor product recommendations, driving conversions and maximizing customer retention.
Now that you’ve understood what is e-commerce, let’s define m-commerce.
What Is M-Commerce?
M-commerce (mobile commerce) refers to commercial transactions that take place via mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. Mobile commerce allows businesses to engage customers on the go, offering frictionless purchasing experiences and personalized notifications.
Here’s a quick example reflecting the m-commerce definition.
FoodHub, a food delivery service, allows users to order meals directly through its mobile app. It streamlines the ordering and payment process, offering a fast, mobile-first experience that suits busy consumers.
Now that we’ve explained the definition of m-commerce, let’s understand its key types.
Types of M-Commerce
M-commerce can be broken down into the following three main categories. Each encompasses various growth areas reshaping how consumers interact with businesses through mobile devices.
1. Mobile Shopping
This refers to purchasing products or services through mobile apps or mobile-optimized websites. Mobile shopping is experiencing rapid growth due to its convenience and efficiency.
It can be divided into two categories.
- In-App Purchasing: This refers to buying products directly within mobile apps. For instance, Amazon’s app allows users to browse, select, and purchase products all within a single mobile interface.
- Virtual Marketplace Apps: This enables consumers to shop items from distinct categories via multiple sellers through mobile apps. For instance, Amazon’s mobile app supports a vast marketplace for various products, from electronics to groceries.
2. Mobile Payments
This involves transactions through mobile devices, streamlining the payment process for online and in-store purchases.
Mobile payments can be further divided into two categories.
- Digital Payment Services: Services such as Apple Wallet, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay enable users to make secure payments through their mobile phones. This enhances their convenience and security.
- Mobile Ticketing: This method involves purchasing and managing tickets for events, travel, or services directly via mobile apps. Mobile ticketing simplifies the ticketing process and eliminates the need for physical tickets.
3. Mobile Banking
This provides users access to their financial accounts through mobile devices, allowing them to perform various banking activities on the go. It offers features, such as checking balances, transferring funds, and paying bills from a mobile device. This makes financial management more accessible.
For instance, PayPal’s mobile app allows users to manage their accounts, transfer funds, and make payments directly from their smartphones.
Benefits of M-Commerce
Here are the key benefits of mobile commerce.
- Efficiency: One-click ordering, mobile wallets, and quick payments reduce transaction friction.
- On-the-Go Accessibility: Consumers can purchase and engage with brands wherever they are, without requiring a desktop.
- Personalized Experience: Location-based features in the mobile app can help provide targeted promotions or offers based on a customer’s region or purchasing behavior.
- Enhanced User Engagement: Mobile apps enable direct communication with customers through in-app messaging and notifications.
- Improved Customer Retention: The convenience of mobile shopping increases brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
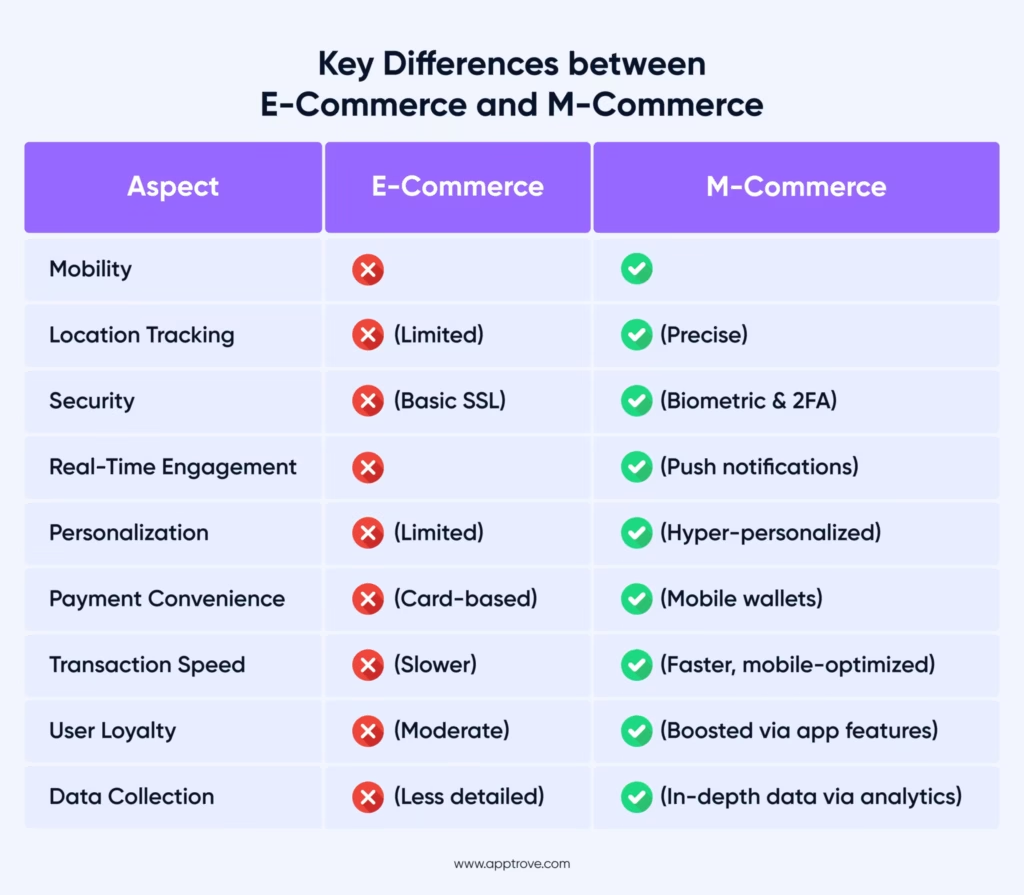
The Core Factor: Difference Between eCommerce and mCommerce
You would have understood e-commerce and m-commerce meaning by now. Let’s now discuss the key differences between m-commerce and e-commerce.
1. Mobility
As discussed, e-commerce transactions primarily happen through desktops and laptops. This means the users typically need to be in a specific place to buy online. This lack of portability makes it less convenient for users on the go.
This can lead to lost opportunities as users may abandon transactions if they cannot complete them quickly.
On the other hand, m-commerce capitalizes on the mobility of mobile phones, tablets, and handy smartwatches. This makes it easier for them to do transactions anywhere and anytime.
For instance, an iGaming mobile app can allow users to easily make in-app purchases or deposit funds through their mobile devices while commuting or relaxing.
2. Location Tracking
E-commerce platforms come with limited location tracking capabilities. They often rely on IP addresses or manually inputted data to track user’s location.
For instance, an e-commerce clothing store uses IP addresses to approximate user locations for shipping information.
However, this limits the ability to provide hyper-localized offers.
M-commerce apps, however, can track users’ exact locations through Wi-Fi and GPS. This allows businesses to provide hyper-personalized, location-specific recommendations and offers.
For instance, a banking app can use GPS to target users based on their real-time location and send tailored loan offers to users who frequently visit areas with high property values. This can boost user engagement and sales.
3. Security
Security is the most crucial aspect of online transactions.
E-commerce platforms leverage traditional measures like SSL encryption and credit card-based transactions. While these measures are effective, 59% of consumers still have concerns about sharing sensitive information online. They feel worried about online payment fraud.
M-commerce takes security a notch higher by incorporating biometric authentication methods such as facial recognition or retina scans.
Here’s a quick example of m-commerce.
Most mobile payment apps like Paytm or Google Pay leverage biometric authentication such as fingerprint scans or face IDs. Besides, users get additional security layers with mobile-specific features like two-factor authentication. This reduces the risk of fraud and increases user trust in high-value mobile transactions.
Here’s a quick summary highlighting the key differences between e-commerce and m-commerce.
Go Mobile with Your Online Business: Key Considerations
As mobile commerce (m-commerce) continues to rise, industry leaders like Amazon, Walmart, and Target invest in their mobile apps to enhance user engagement and loyalty.
It’s high time you go mobile. Adapt and optimize mobile strategies to capture your audience’s data and drive customer retention.
Here’s how to get started.
1. Make Your Website Mobile-Friendly
Google’s “mobile-first indexing” prioritizes mobile-optimized websites in search rankings as they improve user experience.
So, ensure your business website is fully optimized for mobile users. Create a responsive design that adjusts and optimizes its layout, content, and functionality to suit different screen sizes and devices, especially mobile phones and tablets.
Besides, optimize imagery and scripts on your site to reduce page load times on mobile devices. This will ensure that users can smoothly browse products, view details, and complete purchases without friction.
The outcome? Improved customer acquisition and retention.
2. Offer Instant Messaging
A recent study by Jay Baer states that customers value speedy communication.
It further affirms that the speed of response influences customers’ decision to choose a business. 50% of customers are less likely to spend if a business responds slower than expected.
Therefore, integrating live chat support or SMS messaging on your mobile website or app can be a game-changer.
It can provide quick, real-time assistance that aligns with customers’ desire for instant resolutions. Besides live chat, you can use chatbot support to answer common queries of your customers outside business hours. This can lead to higher engagement and satisfaction.
3. Invest in Geofencing
Geofencing is a powerful tool for location-based marketing. It creates virtual boundaries that trigger targeted actions when users enter or exit specific areas.
This means you can deliver tailored promotions and alerts based on user location.
For instance, if you’re a marketing manager at a mobile app company, you could set up geofences around key events or popular venues.
When users enter these premises, they could receive push notifications like, “Check out our exclusive app features available only at this event!”
This can drive engagement and encourage app downloads, thus enhancing your user acquisition strategy.
4. Create a Mobile App
A dedicated mobile app offers several benefits, including exclusive in-app promotions and enhanced customer engagement.
You can also integrate in-app advertising to generate additional revenue and reach targeted audiences within your app.
For instance, an e-commerce brand might offer app-exclusive discounts or rewards to users, while strategically placed in-app ads can provide further monetization opportunities.
Mobile apps can also facilitate direct communication through in-app messaging, further enhancing customer support.
So, determine key features, such as in-app purchases, loyalty rewards, personalized notifications, and opportunities for in-app advertising, and develop a mobile app for your business.
Leveraging social media channels can help drive app downloads and engagement.
5. Leverage the Power of Detailed Analytics with an MMP
Tracking and analyzing mobile marketing efforts is the key to achieving the best outcomes. However, businesses often face challenges, such as fraud risks, inaccurate attribution, and more.
A Mobile Measurement Partner (MMP) can help overcome these challenges by offering real-time insights, fraud detection, and precise attribution across multiple channels.
The right MMP can provide insights into user behavior, campaign performance, and ROI. This can help you refine business strategies and maximize effectiveness.
Why Choose Apptrove?
Our advanced MMP offers tailored insights to boost app installs, improve ROI, and enhance customer lifetime value (LTV).
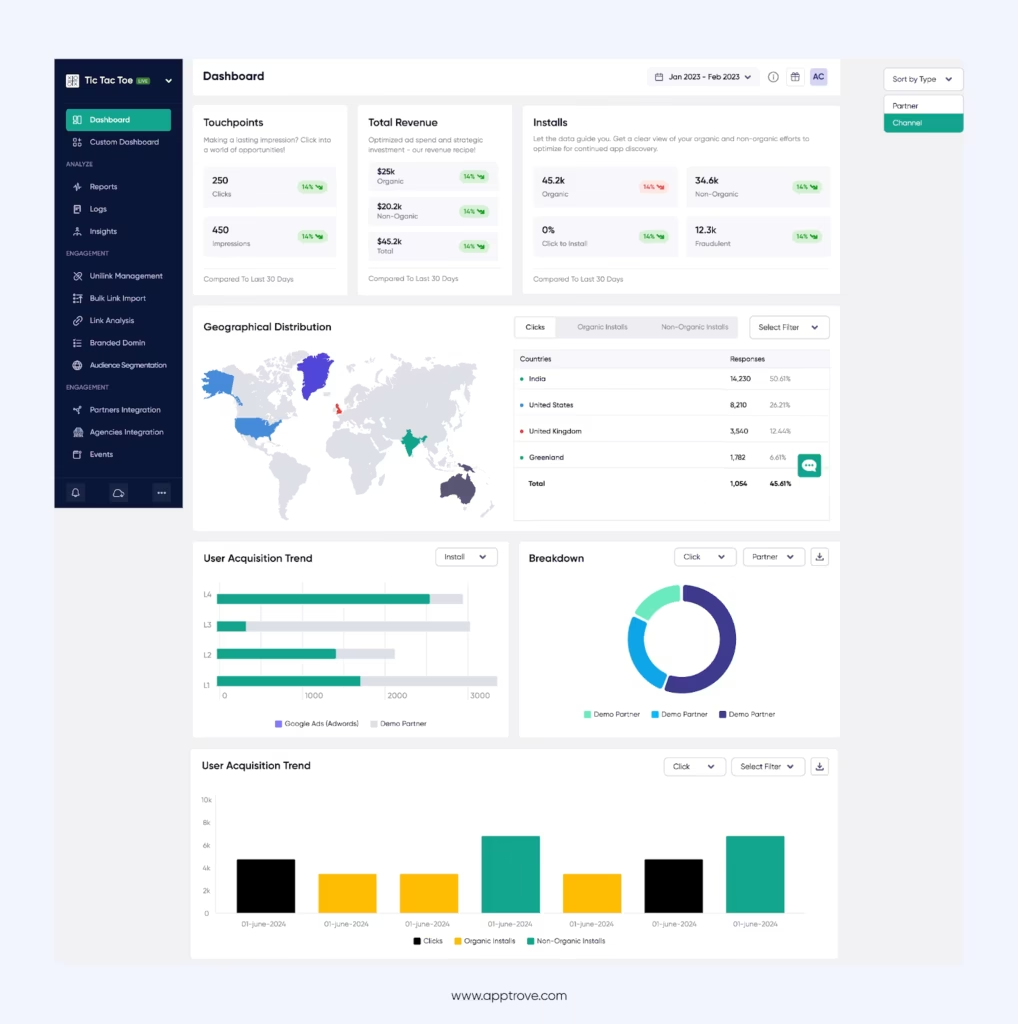
Apptrove offers –
- Real-time ROI Measurement: You gain access to automated reports, granular logs, and advanced cross-device, cross-channel attribution with a unified dashboard. With real-time reports, you can track every dollar spent and focus your budget on where it delivers the highest ROAS.
- Advanced Audience Segmentation: Our MMP supports hyper-targeted campaigns for better user retention. Apptrove provides granular filters and custom cohorts, letting you tailor user experiences and drive higher LTV through focused segmentation.
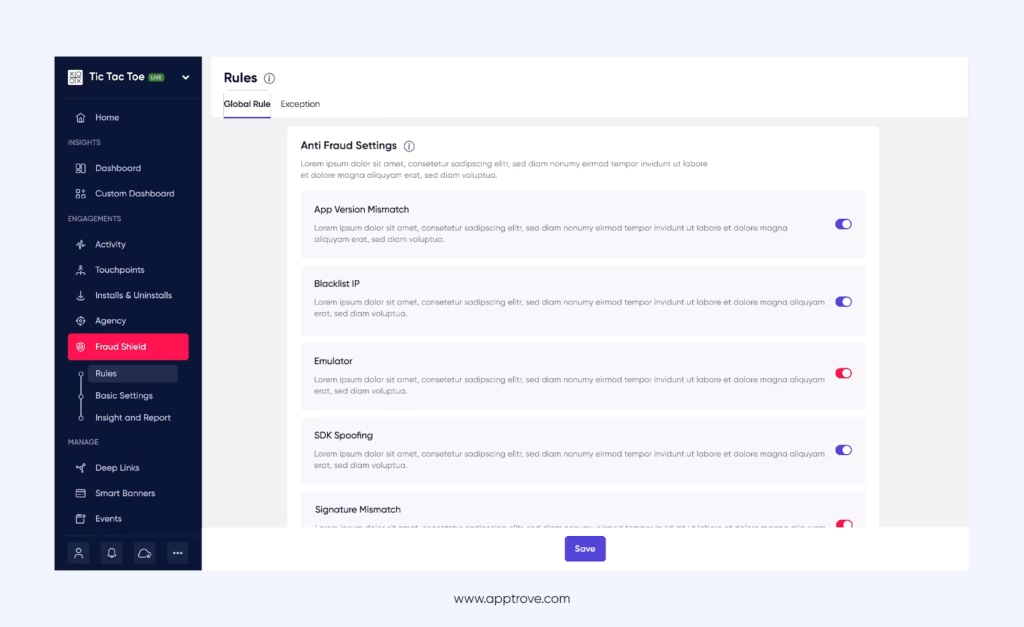
- Robust Fraud Prevention: Its custom fraud shield offers multi-layer protection with custom rules, real-time alerts, and defense against emulator devices, IP duplication, and more. With this advanced customization, you can tailor attribution windows and block fraudulent traffic with validation rules.
- Effective iOS 14+ Measurement: SKAN analytics provide in-depth insights into iOS acquisition and engagement. It is compliant with GDPR-CCPA and e-privacy regulations. Besides, it ensures data security across platforms with industry-standard encryption, regular audits, and penetration testing.
- Intuitive Deep Linking Capabilities: It helps unify customer journeys with customizable deep linking to measure return on experience (ROX).
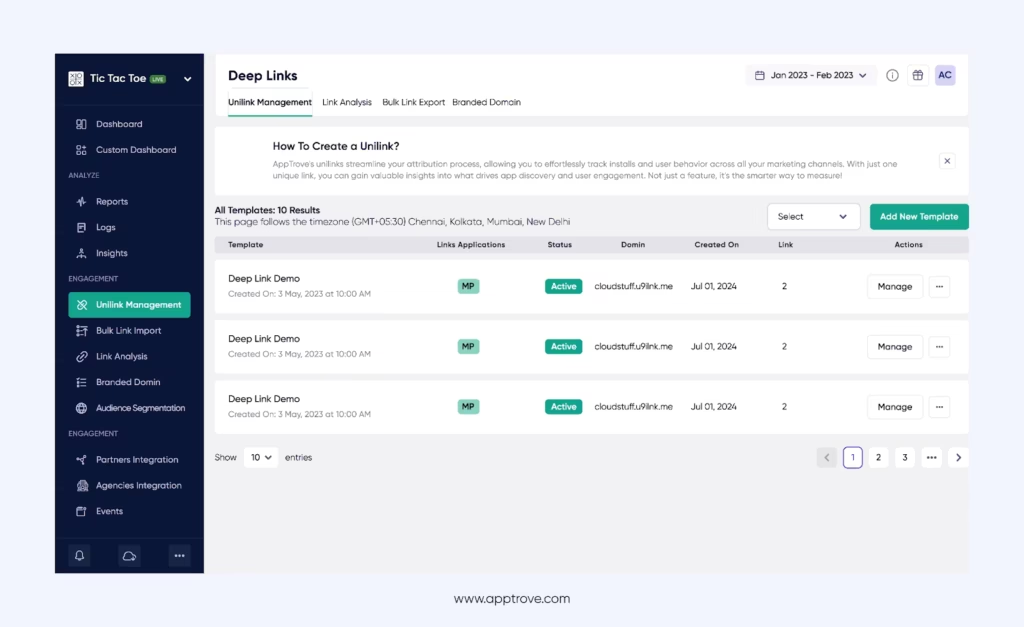
What’s more? Our platform’s user-friendly dashboard, lightweight SDK, and quick global ad network integrations make it easy to use, cutting down on onboarding time.
The best part? Our team provides 24/7 support and local expertise across 11 languages to ensure seamless migration and ongoing assistance globally.
Summing Up
While e-commerce dominates desktop transactions, m-commerce capitalizes on the growing use of mobile devices, offering on-the-go convenience, personalized experiences, and advanced security features.
We are sure this post has clarified the difference between e-commerce and m-commerce for you.
Now, as mobile usage experiences exponential growth, it’s crucial to understand m-commerce’s advantages and disadvantages.
Adopting mobile-first strategies shared in this post can help you capitalize on mobile commerce’s benefits while addressing its challenges.
At Apptrove, we believe in simplifying mobile measurement. We can help you make data-driven decisions without hassles. Get in touch with us to fuel your mobile marketing efforts or sign up for a free trial to experience Apptrove’s offerings.
FAQs
What is the main difference between e-commerce and m-commerce?
E-commerce generally refers to online shopping conducted through desktops and laptops, where users access websites to browse products, make purchases, and complete transactions. M-commerce, on the other hand, focuses on mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. It allows consumers to shop, pay, and interact with brands on the go, often using apps or mobile-optimized websites. The key difference lies in mobility and accessibility—m-commerce enables instant transactions from anywhere, often with features like push notifications, in-app offers, and mobile wallets, creating a faster and more personalized shopping experience.
What are the benefits of m-commerce for businesses?
M-commerce provides several advantages beyond traditional e-commerce. Businesses can engage users anytime and anywhere, offering convenience and immediacy. Features like location-based promotions, in-app messaging, and personalized recommendations help increase user engagement and retention. Mobile apps allow one-click ordering, quick payments, and loyalty programs that drive repeat purchases. Additionally, mobile platforms enable companies to collect rich data on consumer behavior, helping refine marketing strategies and improve ROI. Overall, m-commerce helps businesses create a seamless, frictionless experience that aligns with the fast-paced lifestyle of modern consumers.
How can businesses ensure security in m-commerce transactions?
Security is critical for online transactions, especially on mobile devices. M-commerce platforms often use SSL encryption for data protection and incorporate advanced authentication methods such as fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or two-factor verification to verify users. Additionally, mobile payment systems like Apple Pay or Google Pay have built-in fraud detection and tokenization, which reduces the risk of sensitive information being exposed. Businesses can also implement secure in-app payment gateways, regular security audits, and real-time monitoring to detect unusual activities, ensuring users feel safe while conducting transactions on mobile platforms.
Should businesses invest in both e-commerce and m-commerce platforms?
Investing in both platforms is increasingly essential. While desktops and laptops remain relevant for detailed research, comparisons, or B2B transactions, mobile devices dominate daily consumer interactions. A combined strategy allows businesses to reach a wider audience and adapt to user preferences. E-commerce platforms provide a comprehensive browsing and purchasing environment, while m-commerce delivers convenience, speed, and personalized experiences. By maintaining both, businesses can create an omnichannel approach that maximizes engagement, boosts sales, and ensures that users have a consistent experience across devices.






